What Is a Requirements Traceability Matrix? (With Examples and Best Practices)
Projects fail all the time, not because engineers lack talent, but because requirements get lost in the shuffle. Without a clear way to track what needs to be built, why it matters, and how it will be verified, even well-funded, technically sound programs risk delays, cost overruns, or worse: mission failure.
If you’ve ever wondered what a requirement traceability matrix is, it’s a structured document that maps each project requirement to the corresponding test cases, design elements, and verification steps that confirm it’s been met. In many projects, you’ll also hear this referred to as an RTM, so when someone asks what RTM is, they’re simply using the acronym for requirements traceability matrix.
In high-stakes industries like aerospace, defense, medical devices, or energy, this traceability isn’t just best practice - itt’s mandatory. Teams must prove to regulators, auditors, and customers that every system requirement has been validated. And yet, most are still wrangling massive spreadsheets or outdated PDFs to get it done.
In this guide, we’ll break down what a requirements traceability matrix is, how it’s structured, why it matters, and how teams can build one that stands up to both technical complexity and compliance demands. We’ll also explore tools that make it easier, including how Stell automates this process from day one.
What Is a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)?
Simple Definition and Purpose
A requirements traceability matrix (RTM) is a structured document that maps each project requirement to the corresponding test cases, design elements, and verification steps that confirm it’s been met.
Think of it as a living checklist that tracks requirements from initial definition through design, development, and final validation. It provides visibility into whether each requirement has been fulfilled and how.
This level of traceability is essential in complex or regulated projects, where teams must prove that every regulatory requirement, customer spec, or internal goal has been fully addressed. Without it, gaps in testing, unclear responsibilities, or missed requirements can lead to costly rework, compliance risks, or system failure.
An RTM ensures nothing falls through the cracks, helping teams build systems that are safe, auditable, and ready for launch.
How RTMs Fit into Project Management
A requirements traceability matrix supports the full project lifecycle, from initial scoping and planning through design, testing, and final delivery. No matter the methodology - Agile, Waterfall, or hybrid - RTMs help teams stay aligned on what needs to be built and how success will be verified.
In Agile environments, RTMs can link user stories to test cases and acceptance criteria across iterative sprints. In Waterfall projects, they offer structured, end-to-end traceability from specification to validation.
Typical users of RTMs include systems engineers, test engineers, project managers, quality assurance teams, and compliance leads. These stakeholders rely on traceability matrices to ensure coverage, reduce rework, and demonstrate alignment with regulatory requirements or customer goals.
RTMs are more than documentation; they’re an active tool for driving accountability and delivery across the entire development process.
Core Benefits
A well-structured requirements traceability matrix offers clear, measurable advantages, especially in high-stakes or regulated projects. An RTM:
Prevents scope creep: By tying project deliverables to an approved requirement, the requirements traceability matrix keeps the team focused on what's in scope and flags out-of-scope requests early.
Improves test coverage: Every project requirement is linked to one or more test cases, ensuring nothing is left unverified.
Ensures compliance with regulatory standards: Requirements traceability matrices help teams meet regulatory compliance by documenting how each requirement is validated, creating a clear audit trail.
Provides clarity to stakeholders: The requirements traceability matrix offers a single source of truth for engineers, testers, and program managers, making progress and gaps easy to spot.
Supports change management: When requirements shift, the requirements traceability matrix shows which test cases, components, and documents are affected, enabling faster, safer updates.
Reduces risk and rework: Gaps in verification or missed requirements can delay programs. Requirements traceability matrices help catch those issues early.
Usefulness in Compliance-Heavy Industries
Industries like aerospace, defense, healthcare, and medical devices depend on requirements traceability to ensure safety and regulatory compliance with industry standards. In these sectors, a requirements traceability matrix is not optional. It is often required to pass audits or meet strict regulatory standards like ISO 9001, FDA 21 CFR Part 11, or DO-178C.
Requirements traceability matrices provide the documented evidence regulators need to verify that systems were built and tested as intended. For teams handling classified data or regulated workflows, Stell’s approach to security ensures compliance without compromising performance.
Anatomy of a Requirements Traceability Matrix
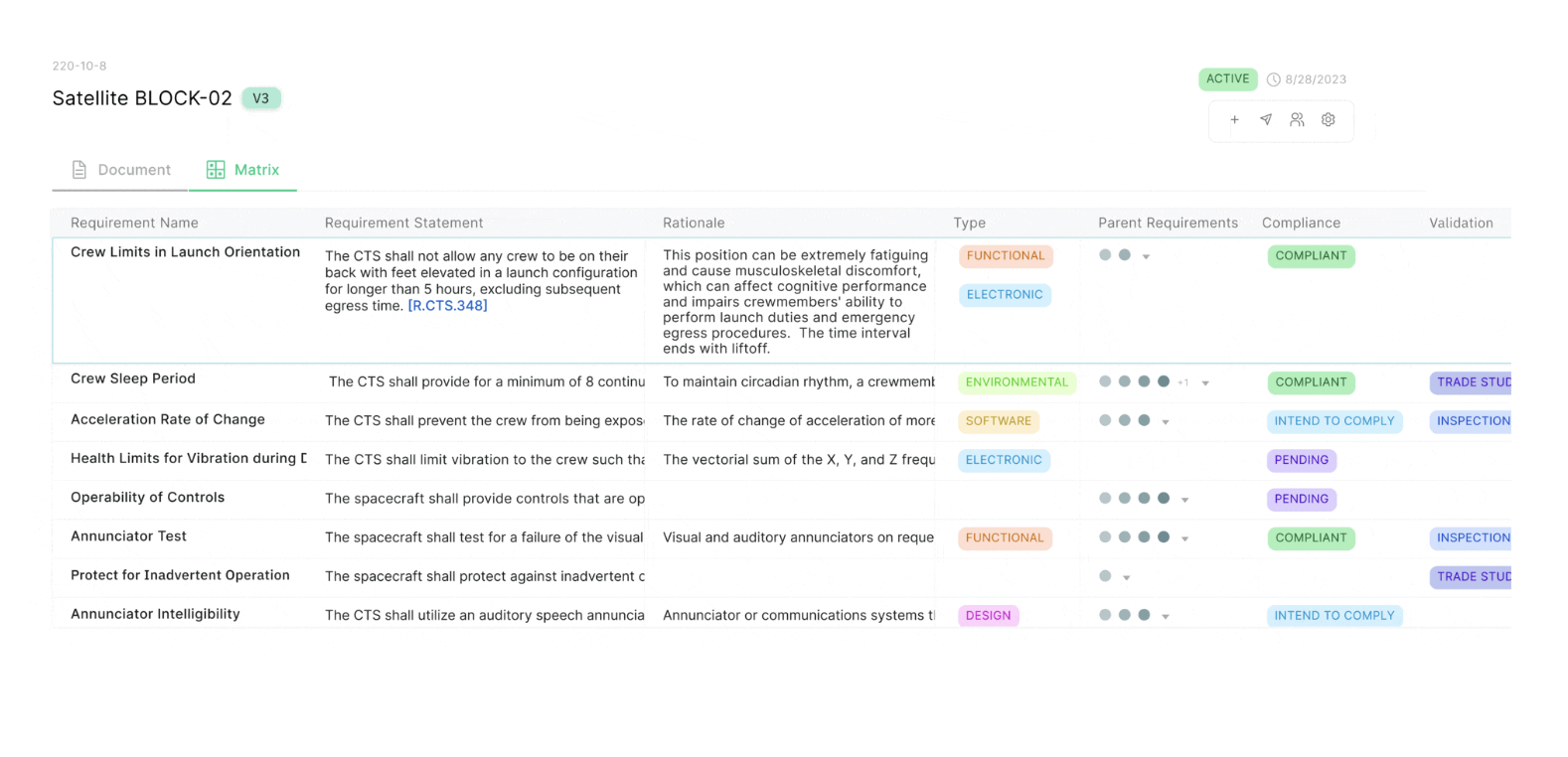
A requirements traceability matrix is typically structured as a spreadsheet or a table within a requirements management tool. It maps each requirement to its corresponding test cases, design elements, and verification steps. This structure helps teams ensure completion of all testing and easy bidirectional traceability throughout the development lifecycle.
Common Columns and Structure
A requirements traceability matrix is typically organized as a table with standardized columns that form the essential components teams need to track each project requirement through validation. While structures may vary by project or tool, most traceability matrices include the following core fields:
Requirement ID: A unique identifier for each requirement, used for reference and traceability.
Requirement name: A short, descriptive title for the requirement.
Shall Statement: A brief but detailed description of what the requirement entails.
Source: Where the requirement originated, such as a stakeholder, contract, business requirement document, or system specification.
Parent Requirements: Higher-level requirements that this one supports.
Child Requirements: Lower-level requirements derived from this one.
Validation: The method used to confirm the requirement meets its intended purpose, such as Inspection, Analysis, or Trade Study.
Verification method: How the requirement will be confirmed, such as inspection, analysis, or testing.
Status: Indicates whether the requirement is pending, in progress, or verified.
Owner or responsible party: The person or team accountable for fulfilling the requirement.
The matrix can be expanded to include fields like risk level, requirement type, or priority, depending on project complexity.
Real-World Use Cases for RTMs
Project Scenarios
A requirements traceability matrix is most valuable when applied to real-world projects where precision and verification are critical.
Software testing: Mapping user stories to test cases ensures that every feature request has a corresponding validation step before release.
Medical device development: Tracing regulatory requirements to design outputs and verification activities helps teams demonstrate full FDA compliance.
Systems engineering: Linking features from initial specifications through design, integration, and validation ensures no requirement is overlooked in complex systems like satellites, aircraft, or defense platforms.
In each case, the requirements traceability matrix keeps teams aligned, strengthens test coverage, and provides the documented proof needed for audits or customer sign-off.
Industry-Specific Benefits
In regulated industries such as aerospace, defense, healthcare, and medical devices, a requirements traceability matrix delivers far more than project organization. It provides legal defensibility, complete documentation for regulatory requirements, and ongoing support for process improvement across the entire project lifecycle.
Legal defensibility: A requirements traceability matrix creates a permanent record linking project requirements to test cases and results, demonstrating due diligence in disputes or investigations.
Documentation for compliance audits: Traceability matrices give auditors clear, verifiable proof that every requirement has been validated, supporting standards like ISO 9001, FDA 21 CFR Part 11, and DO-178C.
Support for continuous improvement: Analyzing traceability data after delivery helps identify missed test coverage, reduce rework, and improve future programs.
By ensuring no requirement is overlooked, a requirements traceability matrix can prevent costly failures and protect mission success.
Step-by-Step Instructions
If you’re wondering how to create a requirements traceability matrix, the process is straightforward, but doing it well ensures complete test coverage, clear accountability, and smooth compliance audits. Follow these steps to create a requirements traceability matrix that works across your entire project lifecycle.
Define scope and objectives: Clarify which systems, subsystems, project goals, and stakeholders the requirements traceability matrix will cover. This keeps effort focused and measurable.
Collect project requirements and sources: Pull requirements from contracts, specs, user stories, and stakeholder interviews. Record the source to support audits and reviews.
Choose a format and tool: Start in a spreadsheet or set it up in a requirements management platform or your project management software. Pick what your team will actually maintain and customize with the specific features you need.
Standardize columns: Include Requirement ID, description, source, related test cases, verification method, status, and owner. Consistent fields make the matrix searchable and auditable.
Establish bidirectional traceability: Create links from requirement to test (forward traceability) and from test back to requirement (backward traceability). This confirms full test coverage and prevents orphan tests.
Map verification and acceptance criteria: Define how each requirement will be verified - inspection, analysis, demonstration, or test results. Record pass or fail criteria.
Assign ownership: Name the engineer or team responsible for each line item. Clear ownership speeds decisions and closes gaps.
Review with QA and compliance: Quality assurance teams validate that the matrix meets regulatory compliance to ensure compliance and supports your audit trail.
Integrate with delivery workflows: Link the matrix to issues, builds, and test runs in your project management tool. Keep it active through the development lifecycle.
Maintain change control: When requirements evolve, run impact analysis to update linked test cases and status. Healthy traceability matrices evolve across the development cycle and the product development process.
Frequent Pitfalls
Even a well-designed requirements traceability matrix can fail if it’s not maintained correctly. Common mistakes include:
Incomplete or vague requirements: Ambiguity makes it impossible to create test cases or verification steps.
Forgetting to update during changes: Outdated traceability matrices lead to missed requirements and failed audits, making proving compliance difficult.
Not involving QA or test teams early: Early collaboration with multiple stakeholders ensures requirement coverage and realistic validation plans to maintain quality standards.
Using inconsistent formats: Non-standardized fields make searching, sorting, status tracking, and auditing more difficult.
Overcomplicating the structure: Adding unnecessary columns or details can make tracking progress while using the matrix hard to maintain.
Pro Tips to Prevent Failure
To keep your requirements traceability matrix accurate and valuable throughout the duration of complex projects, apply these best practices:
Use templates or dedicated tools: Standardized formats reduce errors and speed setup.
Assign clear ownership: Project managers ensure the matrix is updated after every change.
Review regularly: Include the matrix in sprint planning, milestone reviews, or QA checkpoints.
Automate status tracking: Link to your project management tool to update progress automatically.
Keep it simple: Avoid unnecessary columns or data points that complicate determining the project status.
How RTMs Support Regulatory Compliance
Standards and Frameworks
A requirements traceability matrix is a critical tool for aligning business objectives, project goals, and business requirements while meeting legal and regulatory standards such as:
ISO 9001 and ISO 13485 for quality management in manufacturing and medical devices
FDA 21 CFR Part 11 for electronic records and signatures in regulated industries
DO-178C for airborne systems and software in aviation
NASA-STD-5019 for fracture control requirements in space flight hardware
MIL-STD-810 for environmental testing of defense hardware under extreme conditions
By mapping test cases to specific requirements and maintaining clear traceability links, teams can show how they track requirements from definition through verification. This documentation not only satisfies legal guidelines but also provides auditable proof during compliance reviews, helping organizations respond quickly and effectively to regulator questions.
Documentation and Auditing
A requirements traceability matrix streamlines audits by acting as a single source of truth for project documentation, tracking requirements, business requirements, and traceability links. Both a forward traceability matrix, a backward traceability matrix, and a reverse traceability matrix help auditors see how requirements connect to mapping test cases, verification methods, and test results. Keeping all documentation in one place reduces audit preparation time and ensures compliance with legal guidelines and industry standards.
Tools for Creating and Managing RTMs
Manual Tools vs. Software Solutions
Teams often start building a requirements traceability matrix in Excel or Google Sheets. Excel offers flexibility but is prone to manual errors and version control issues. Google Sheets allows real-time collaboration but lacks automation, advanced reporting, and built-in compliance features.
While these manual methods work for small projects, they quickly become inefficient and risky at scale. Tracking thousands of requirements, maintaining traceability links, and managing both a forward traceability matrix and a backward traceability matrix across the entire project scope becomes cumbersome without automation or the ability to quickly generate reports.
Stell is a purpose-built requirements traceability solution designed for compliance-heavy industries. It provides automated requirement-to-test linking, version tracking, and support for meeting industry standards. This makes it easier to stay audit-ready, remain aligned with customer and regulatory expectations throughout the development cycle, and ensure both project success and customer satisfaction. Stell also integrates with application lifecycle management platforms, project management tools, and testing frameworks to keep requirements, test cases, and verification results connected across the entire project scope.
Turn Traceability into a Competitive Advantage
A well-built requirements traceability matrix drives project success by aligning business goals, project goals, and project scope, ensuring complete requirement coverage, maintaining compliance, and giving teams full visibility across the project lifecycle. It reduces the risk of missed requirements, costly rework, and failed audits. Without one, teams face unclear accountability, slower delivery, and greater exposure to compliance failures.
With Stell’s purpose-built RTM solution, you can align business goals with customer and regulatory expectations, meet project expectations, maintain accurate traceability links in a bidirectional traceability matrix, and generate reports that stand up to any audit.